AABB Tree
官方文档链接:CGAL 5.5 - 3D Fast Intersection and Distance Computation (AABB Tree): User Manual
1 介绍
AABB树提供了一个静态的数据结构和算法,能够对有限3D几何对象集合进行高效的相交和距离查询。
- 相交查询可以是任何类型,前提是在traits类中实现了相应的交集谓词和构造函数。
- 距离查询仅限于点的查询。
AABB树的数据结构将几何数据的迭代器范围作为输入,然后将其转换为primitives(图元)。在这些primitives中,构造了一个轴对齐边界框(axis-aligned bounding boxes)(AABB)的层次结构,用于加速相交和距离查询。每个图元都能访问一个输入几何对象(datum)和该对象的参考id。例如,一个图元将3D triangle作为datum,多面体表面的face handle作为id。而通过AABB tree进行相交和距离查询时,返回值中就包含了相交对象/最近点和相交图元id/最近图元id。
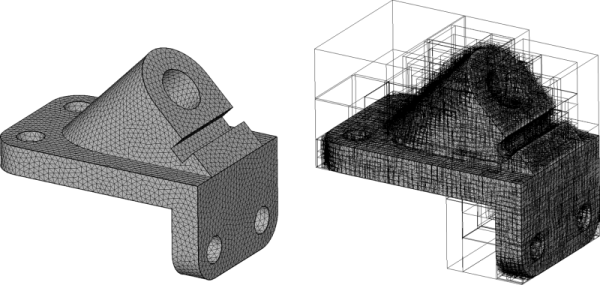
左图为表面三角网格模型,右图为其构建的AABB树。
2 接口
相交:
AABB_tree::do_intersect()-
AABB_tree::number_of_intersected_primitives()
-
AABB_tree::all_intersected_primitives()
-
AABB_tree::any_intersected_primitive()
-
AABB_tree::first_intersected_primitive()
以上函数不会构造相交对象,仅做测试。
-
AABB_tree::all_intersections()
-
AABB_tree::any_intersection()
-
AABB_tree::first_intersection()
以上函数会构造相交的对象。
距离:
-
AABB_tree::closest_point()
-
AABB_tree::closest_point_and_primitive()
-
AABB_tree::accelerate_distance_queries()
注意,在AABB Tree中应避免出现退化的图元,防止算法出错。
3 几个栗子
下面例子中,三维三角形集合以list的形式存储。AABB图元将三角形(triangle)作为datum(数据),list里的迭代器作为id。程序中实现了射线与三角形集合的相交查询,点与三角形集合的最近点查询和距离计算。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_tree.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_traits.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_triangle_primitive.h>
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> K;
typedef K::FT FT;
typedef K::Ray_3 Ray;
typedef K::Line_3 Line;
typedef K::Point_3 Point;
typedef K::Triangle_3 Triangle;
typedef std::list<Triangle>::iterator Iterator;
typedef CGAL::AABB_triangle_primitive<K, Iterator> Primitive;
typedef CGAL::AABB_traits<K, Primitive> AABB_triangle_traits;
typedef CGAL::AABB_tree<AABB_triangle_traits> Tree;
int main()
{
Point a(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Point b(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
Point c(0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
Point d(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
std::list<Triangle> triangles;
triangles.push_back(Triangle(a,b,c));
triangles.push_back(Triangle(a,b,d));
triangles.push_back(Triangle(a,d,c));
Tree tree(triangles.begin(),triangles.end());
Ray ray_query(a,b);
std::cout << tree.number_of_intersected_primitives(ray_query)
<< " intersections(s) with ray query" << std::endl;
Point point_query(2.0, 2.0, 2.0);
Point closest_point = tree.closest_point(point_query);
std::cerr << "closest point is: " << closest_point << std::endl;
FT sqd = tree.squared_distance(point_query);
std::cout << "squared distance: " << sqd << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
|
在下面这个例子中,将创建一个多面体三角面片的AABB树。其中,AABB图元将三角形面片句柄包装为id,对应的面片作为几何对象(datum)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_tree.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_traits.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_face_graph_triangle_primitive.h>
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> K;
typedef K::Point_3 Point;
typedef K::Plane_3 Plane;
typedef K::Vector_3 Vector;
typedef K::Segment_3 Segment;
typedef K::Ray_3 Ray;
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<K> Polyhedron;
typedef CGAL::AABB_face_graph_triangle_primitive<Polyhedron> Primitive;
typedef CGAL::AABB_traits<K, Primitive> Traits;
typedef CGAL::AABB_tree<Traits> Tree;
typedef boost::optional< Tree::Intersection_and_primitive_id<Segment>::Type > Segment_intersection;
typedef boost::optional< Tree::Intersection_and_primitive_id<Plane>::Type > Plane_intersection;
typedef Tree::Primitive_id Primitive_id;
int main()
{
Point p(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Point q(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
Point r(0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
Point s(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Polyhedron polyhedron;
polyhedron.make_tetrahedron(p, q, r, s);
Tree tree(faces(polyhedron).first, faces(polyhedron).second, polyhedron);
Point a(-0.2, 0.2, -0.2);
Point b(1.3, 0.2, 1.3);
Segment segment_query(a,b);
if(tree.do_intersect(segment_query))
std::cout << "intersection(s)" << std::endl;
else
std::cout << "no intersection" << std::endl;
std::cout << tree.number_of_intersected_primitives(segment_query)
<< " intersection(s)" << std::endl;
Segment_intersection intersection =
tree.any_intersection(segment_query);
if(intersection)
{
const Point* p = boost::get<Point>(&(intersection->first));
if(p)
std::cout << "intersection object is a point " << *p << std::endl;
}
std::list<Segment_intersection> intersections;
tree.all_intersections(segment_query, std::back_inserter(intersections));
std::list<Primitive_id> primitives;
tree.all_intersected_primitives(segment_query, std::back_inserter(primitives));
Vector vec(0.0,0.0,1.0);
Plane plane_query(a,vec);
Plane_intersection plane_intersection = tree.any_intersection(plane_query);
if(plane_intersection)
{
if(boost::get<Segment>(&(plane_intersection->first)))
std::cout << "intersection object is a segment" << std::endl;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
|
下面例子先读取一个闭合的多面体表面,然后以每个face的重心为起始点和垂直于face向模型内部的方向作射线,进行一个ray shooting query。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_tree.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_traits.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_face_graph_triangle_primitive.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/compute_normal.h>
#include <CGAL/Polygon_mesh_processing/orientation.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> K;
typedef K::FT FT;
typedef K::Point_3 Point;
typedef K::Vector_3 Vector;
typedef K::Ray_3 Ray;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh<Point> Mesh;
typedef boost::graph_traits<Mesh>::face_descriptor face_descriptor;
typedef boost::graph_traits<Mesh>::halfedge_descriptor halfedge_descriptor;
typedef CGAL::AABB_face_graph_triangle_primitive<Mesh> Primitive;
typedef CGAL::AABB_traits<K, Primitive> Traits;
typedef CGAL::AABB_tree<Traits> Tree;
typedef boost::optional<Tree::Intersection_and_primitive_id<Ray>::Type> Ray_intersection;
struct Skip
{
face_descriptor fd;
Skip(const face_descriptor fd)
: fd(fd)
{}
bool operator()(const face_descriptor& t) const
{ if(t == fd){
std::cerr << "ignore " << t <<std::endl;
};
return(t == fd);
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
const std::string filename = (argc > 1) ? argv[1] : CGAL::data_file_path("meshes/tetrahedron.off");
Mesh mesh;
if(!CGAL::IO::read_polygon_mesh(filename, mesh))
{
std::cerr << "Invalid input." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
Tree tree(faces(mesh).first, faces(mesh).second, mesh);
double d = CGAL::Polygon_mesh_processing::is_outward_oriented(mesh)?-1:1;
for(face_descriptor fd : faces(mesh))
{
halfedge_descriptor hd = halfedge(fd,mesh);
Point p = CGAL::centroid(mesh.point(source(hd,mesh)),
mesh.point(target(hd,mesh)),
mesh.point(target(next(hd,mesh),mesh)));
Vector v = CGAL::Polygon_mesh_processing::compute_face_normal(fd,mesh);
Ray ray(p,d * v);
Skip skip(fd);
Ray_intersection intersection = tree.first_intersection(ray, skip);
if(intersection)
{
if(boost::get<Point>(&(intersection->first))){
const Point* p = boost::get<Point>(&(intersection->first) );
std::cout << *p << std::endl;
}
}
}
std::cerr << "done" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
|
因为重心计算属于浮点运算,因此射线第一个击中的面可能是起点质心所在的面。为了避免此状况,这里需要给first_intersection()传入一个skip functor将此面忽略。
上个例子是计算的射线与mesh的相交,下面这个例子展示如何查询一个点到mesh的squared distance和closest point及其所在的triangle。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
#include <iostream>
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_tree.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_traits.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_face_graph_triangle_primitive.h>
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> K;
typedef K::FT FT;
typedef K::Point_3 Point;
typedef K::Segment_3 Segment;
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<K> Polyhedron;
typedef CGAL::AABB_face_graph_triangle_primitive<Polyhedron> Primitive;
typedef CGAL::AABB_traits<K, Primitive> Traits;
typedef CGAL::AABB_tree<Traits> Tree;
typedef Tree::Point_and_primitive_id Point_and_primitive_id;
int main()
{
Point p(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Point q(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
Point r(0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
Point s(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Polyhedron polyhedron;
polyhedron.make_tetrahedron(p, q, r, s);
Tree tree(faces(polyhedron).first, faces(polyhedron).second, polyhedron);
Point query(0.0, 0.0, 3.0);
FT sqd = tree.squared_distance(query);
std::cout << "squared distance: " << sqd << std::endl;
Point closest = tree.closest_point(query);
std::cout << "closest point: " << closest << std::endl;
Point_and_primitive_id pp = tree.closest_point_and_primitive(query);
Point closest_point = pp.first;
Polyhedron::Face_handle f = pp.second;
std::cout << "closest point: " << closest_point << std::endl;
std::cout << "closest triangle: ( "
<< f->halfedge()->vertex()->point() << " , "
<< f->halfedge()->next()->vertex()->point() << " , "
<< f->halfedge()->next()->next()->vertex()->point()
<< " )" << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
|
最后一个例子,是对于AABB树中图元的增量插入。虽然AABB树是一个静态的数据结构,但是它允许插入primitives(图元)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| #include <iostream>
#include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_tree.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_traits.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
#include <CGAL/AABB_face_graph_triangle_primitive.h>
typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double> K;
typedef K::FT FT;
typedef K::Point_3 Point;
typedef K::Segment_3 Segment;
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<K> Polyhedron;
typedef CGAL::AABB_face_graph_triangle_primitive<Polyhedron, CGAL::Default, CGAL::Tag_false> Primitive;
typedef CGAL::AABB_traits<K, Primitive> Traits;
typedef CGAL::AABB_tree<Traits> Tree;
typedef Tree::Point_and_primitive_id Point_and_primitive_id;
int main()
{
Point p(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Point q(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
Point r(0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
Point s(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Polyhedron polyhedron1;
polyhedron1.make_tetrahedron(p, q, r, s);
Point p2(11.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Point q2(10.0, 1.0, 0.0);
Point r2(10.0, 0.0, 1.0);
Point s2(10.0, 0.0, 0.0);
Polyhedron polyhedron2;
polyhedron2.make_tetrahedron(p2, q2, r2, s2);
Tree tree(faces(polyhedron1).first, faces(polyhedron1).second, polyhedron1);
tree.insert(faces(polyhedron2).first, faces(polyhedron2).second, polyhedron2);
Point query(0.0, 0.0, 3.0);
FT sqd = tree.squared_distance(query);
std::cout << "squared distance: " << sqd << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
|
上面这个例子中,首先使用polyhedron1构建tree,然后使用insert()函数将polyhedron2的faces作为primitives插入到tree中。
