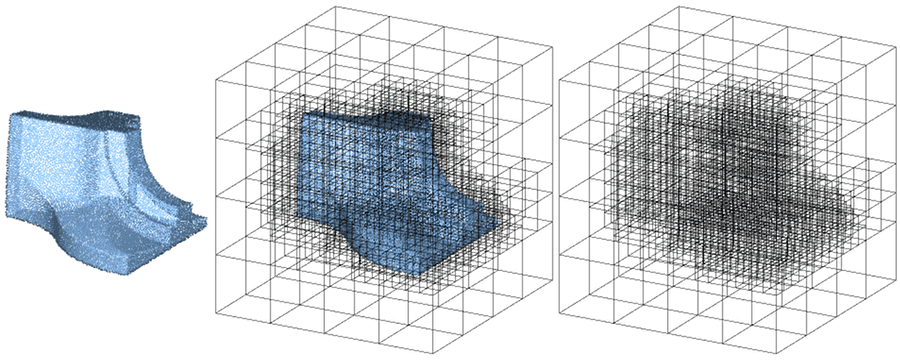
官方文档链接:CGAL 5.5 - Quadtrees, Octrees, and Orthtrees: User Manual
1 概述 1.1 定义 八叉树(Octrees)是一种用于描述三维空间的树状数据结构。八叉树的每个节点表示一个正方体的体积元素,每个节点有八个子节点,将八个子节点所表示的体积元素加在一起就等于父节点的体积。八叉树是四叉树在三维空间上的扩展,二维上我们有四个象限,而三维上,我们有8个卦限。八叉树主要用于空间划分和最近邻搜索。
引用链接:几何体数据结构学习(2)八叉树 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
八叉树(Octrees)属于二维四叉树(Quadtrees)在三维空间上的拓展,同时这种数据统称为正交树(orthtrees)。当维度为4或拓展到更高维的时候,我们称其为”hyperoctree” (超八叉树)。
2 构建 一个正交树通过使用点集进行构建。正交树构造函数直接使用提供的点进行排列,返回一个具有单个root的树。
在构建过程中,会调用refine()方法进一步细分空间。此方法使用split predicate(拆分谓词),该谓词的输入为节点,若该节点应该拆分,则返回true,否则返回false。因此在构建过程中允许用户选择orthtree细化的标准。其中CGAL提供有预定义谓词如Maximum_depth 和 Maximum_number_of_inliers。split predicate是一个用户可定义的functor,用于决定一个节点是否需要拆分。
2.1 一般构建流程:
将当前的立方体细分为八个子立方体。
如果任何一个子立方体内包含多个点,则将其进一步细分为八个子立方体。
重复以上操作使得每个子立方体内包含最多一个点。
2.2 代码示例
这里只涉及八叉树的构建示例。
第一个例子展示了如何从元素为Point_3的向量对象构建八叉树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <iostream> #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h> #include <CGAL/Octree.h> typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double > Kernel;typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;typedef std::list<Point> Point_vector;typedef CGAL::Octree<Kernel, Point_vector> Octree;int main () emplace_back (1 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (2 , 1 , -11 );emplace_back (2 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (1 , -2 , 1 );emplace_back (1 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (-1 , 1 , 1 );Octree octree (points) ;refine (10 , 20 );return EXIT_SUCCESS;
在初始化Octree对象后,紧接着调用了refine()方法进行细分。这里是使用了CGAL默认的拆分谓词,即Maximum_depth_and_maximum_number_of_inliers
1 2 3 void refine (size_t max_depth = 10 , size_t bucket_size = 20 ) refine (Orthtrees::Maximum_depth_and_maximum_number_of_inliers (max_depth, bucket_size));
其中,max_depth为拆分的最大深度,bucket_size为每个节点内点的最大数量。
接下来这个例子中,展示了如何从 Point_set_3 构建一个Octree。与上一个例子不同,Octree的构造形式为Orthtree<Orthtree_traits_3<GeomTraits>, PointRange, PointMap>,上个例子使用了点向量进行构建,属于最简单的构建方法,其中PointMap参数默认为Identity_property_map。而本例中,Point_set_3数据结构要求一个非默认的点映射类型和对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h> #include <CGAL/Octree.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3/IO.h> typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double > Kernel;typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;typedef CGAL::Point_set_3<Point> Point_set;typedef Point_set::Point_map Point_map;typedef CGAL::Octree<Kernel, Point_set, Point_map> Octree;int main (int argc, char **argv) std::ifstream stream ((argc > 1 ) ? argv[1 ] : CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/cube.pwn" )) ;if (0 == points.number_of_points ()) {"Error: cannot read file" << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;"loaded " << points.number_of_points () << " points\n" << std::endl;Octree octree (points, points.point_map()) ;refine (CGAL::Orthtrees::Maximum_depth_and_maximum_number_of_inliers (5 , 10 ));return EXIT_SUCCESS;
所以,这里使用了points.point_map()作为PointMap参数进行构建。
以上两个例子中refine()方法都使用的是默认拆分谓词Maximum_depth_and_maximum_number_of_inliers,在下面这个例子中,展示了如何自定义拆分谓词进行八叉树细分。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h> #include <CGAL/Octree.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3/IO.h> typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double > Kernel;typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;typedef Kernel::FT FT;typedef CGAL::Point_set_3<Point> Point_set;typedef Point_set::Point_map Point_map;typedef CGAL::Octree<Kernel, Point_set, Point_map> Octree;struct Split_by_ratio {size_t ratio;Split_by_ratio (std::size_t ratio) : ratio (ratio) {}template <class Node> bool operator () (const Node &n) const {return n.size () > (ratio * n.depth ());int main (int argc, char **argv) std::ifstream stream ((argc > 1 ) ? argv[1 ] : CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/cube.pwn" )) ;if (0 == points.number_of_points ()) {"Error: cannot read file" << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;"loaded " << points.number_of_points () << " points" << std::endl;Octree octree (points, points.point_map()) ;refine (Split_by_ratio (2 ));return EXIT_SUCCESS;
这个例子中,自定义了一个拆分谓词Split_by_ratio,对每个节点的深度和最大内点数量进行了比例限制,最大内点数量不能大于节点深度与ratio的乘积。
3 遍历 3.1 手动遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h> #include <CGAL/Octree.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3/IO.h> typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double > Kernel;typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;typedef CGAL::Point_set_3<Point> Point_set;typedef Point_set::Point_map Point_map;typedef CGAL::Octree<Kernel, Point_set, Point_map> Octree;int main (int argc, char **argv) std::ifstream stream ((argc > 1 ) ? argv[1 ] : CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/cube.pwn" )) ;if (0 == points.number_of_points ()) {"Error: cannot read file" << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;"loaded " << points.number_of_points () << " points\n" << std::endl;Octree octree (points, points.point_map()) ;refine ();"Navigation relative to the root node" << std::endl;"~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" << std::endl;"the root node: " << std::endl;root () << std::endl;"the first child of the root node: " << std::endl;root ()[0 ] << std::endl;"the fifth child: " << std::endl;root ()[4 ] << std::endl;"the fifth child, accessed without the root keyword: " << std::endl;4 ] << std::endl;"the second child of the fourth child: " << std::endl;root ()[4 ][1 ] << std::endl;"the second child of the fourth child, accessed without the root keyword: " << std::endl;4 ][1 ] << std::endl;3 ][2 ];"Navigation relative to a child node" << std::endl;"~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" << std::endl;"the third child of the fourth child: " << std::endl;"the third child: " << std::endl;parent () << std::endl;"the next sibling of the third child of the fourth child: " << std::endl;parent ()[cur.local_coordinates ().to_ulong () + 1 ] << std::endl;return EXIT_SUCCESS;
从root节点开始,子节点可以通过使用[0~7]操作符进行访问。
对于除root外的节点,可以通过访问方法parent()访问其父节点。
3.2 前序遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h> #include <CGAL/Octree.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3/IO.h> typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double > Kernel;typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;typedef CGAL::Point_set_3<Point> Point_set;typedef Point_set::Point_map Point_map;typedef CGAL::Octree<Kernel, Point_set, Point_map> Octree;typedef CGAL::Orthtrees::Preorder_traversal Preorder_traversal;int main (int argc, char **argv) std::ifstream stream ((argc > 1 ) ? argv[1 ] : CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/cube.pwn" )) ;if (0 == points.number_of_points ()) {"Error: cannot read file" << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;"loaded " << points.number_of_points () << " points\n" << std::endl;Octree octree (points, points.point_map()) ;refine ();for (Octree::Node node : octree.traverse<Preorder_traversal>()) {return EXIT_SUCCESS;
octree.traverse<Preorder_traversal>()输出八叉树的前序遍历迭代器。
3.3 自定义遍历 通过构建 OrthtreeTraversal概念模型,实现自定义遍历策略。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h> #include <CGAL/Octree.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3/IO.h> typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double > Kernel;typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;typedef CGAL::Point_set_3<Point> Point_set;typedef Point_set::Point_map Point_map;typedef CGAL::Octree<Kernel, Point_set, Point_map> Octree;typedef Octree::Node Node;struct First_branch_traversal { Node first (Node root) const {return root;Node next (Node n) const {if (n.is_leaf ())return Node ();return n[0 ];int main (int argc, char **argv) std::ifstream stream ((argc > 1 ) ? argv[1 ] : CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/cube.pwn" )) ;if (0 == points.number_of_points ()) {"Error: cannot read file" << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;"loaded " << points.number_of_points () << " points\n" << std::endl;Octree octree (points, points.point_map()) ;refine ();for (auto &node : octree.traverse<First_branch_traversal>())return EXIT_SUCCESS;
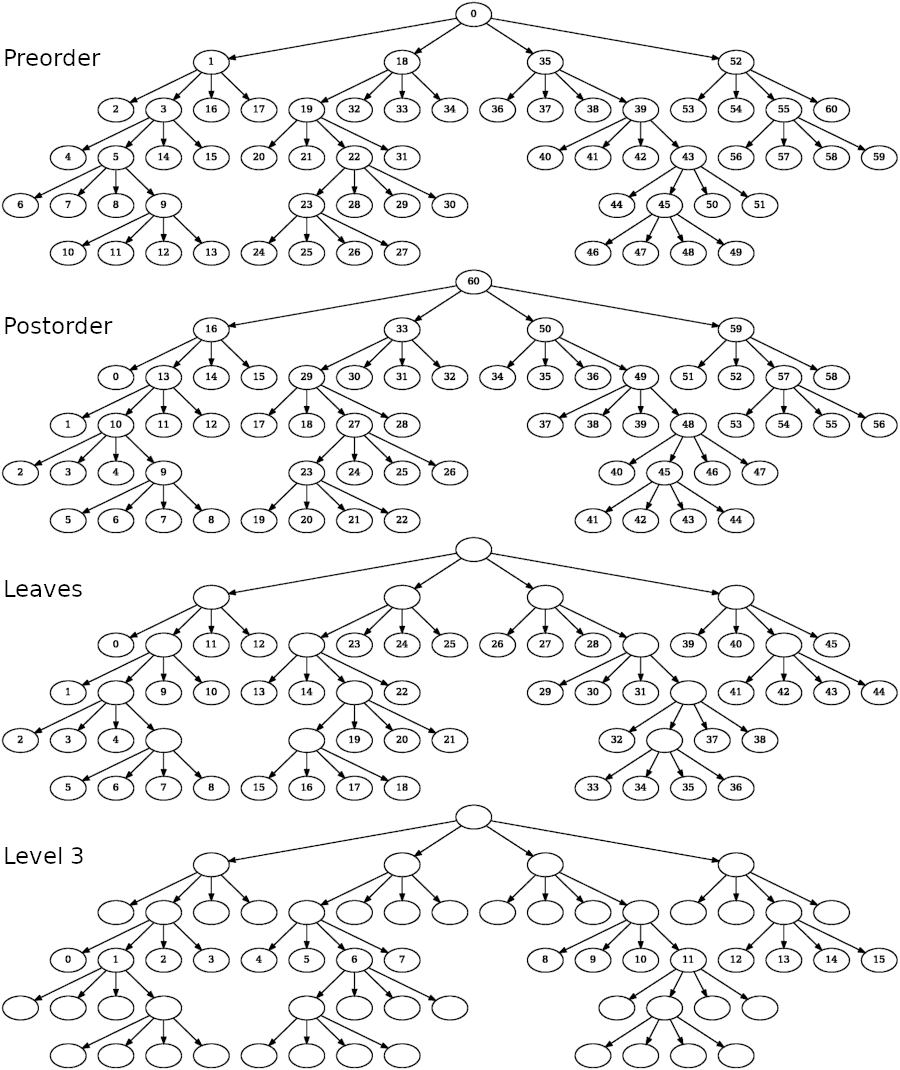
下图展示了不同遍历策略的具体遍历情况。
4 任务加速 构建八叉树的目的在于,可以利用其高效的搜索能力对不同的任务进行加速。
4.1 寻找最邻近点 注意,对于此任务k-d树的加速效果要优于八叉树,实际中首选前者,除非用到八叉树的特有功能。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h> #include <CGAL/Octree.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3.h> #include <CGAL/Point_set_3/IO.h> #include <boost/iterator/function_output_iterator.hpp> typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double > Kernel;typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;typedef CGAL::Point_set_3<Point> Point_set;typedef Point_set::Point_map Point_map;typedef CGAL::Octree<Kernel, Point_set, Point_map> Octree;int main (int argc, char **argv) std::ifstream stream ((argc > 1 ) ? argv[1 ] : CGAL::data_file_path("points_3/cube.pwn" )) ;if (0 == points.number_of_points ()) {"Error: cannot read file" << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;"loaded " << points.number_of_points () << " points" << std::endl;Octree octree (points, points.point_map()) ;refine (10 , 20 );0 , 0 , 0 },1 , 1 , 1 },-1 , -1 , -1 },-0.46026 , -0.25353 , 0.32051 },-0.460261 , -0.253533 , 0.320513 }for (const Point& p : points_to_find)nearest_neighbors 1 , make_function_output_iterator const Point& nearest)"the nearest point to (" << p <<") is (" << nearest << ")" << std::endl;return EXIT_SUCCESS;
4.2 分级 下面例子展示了如何使用分级方法消除八叉树在深度上的大跳跃。其中使用 grade()对八叉树节点进行划分,使相邻节点在深度上的差别不大于1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <iostream> #include <CGAL/Simple_cartesian.h> #include <CGAL/Octree.h> typedef CGAL::Simple_cartesian<double > Kernel;typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;typedef std::vector<Point> Point_vector;typedef CGAL::Octree<Kernel, Point_vector> Octree;int main () emplace_back (1 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (2 , 1 , -11 );emplace_back (2 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (1 , -2 , 1 );emplace_back (1 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (-1 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (-1.1 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (-1.01 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (-1.001 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (-1.0001 , 1 , 1 );emplace_back (-1.0001 , 1 , 1 );Octree octree (points) ;refine (10 , 2 );"\nUn-graded tree" << std::endl;"~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" << std::endl;grade ();"\nGraded tree" << std::endl;"~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~" << std::endl;return EXIT_SUCCESS;